1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| package com.atguigu.rabbitmq.fanout;
import com.atguigu.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
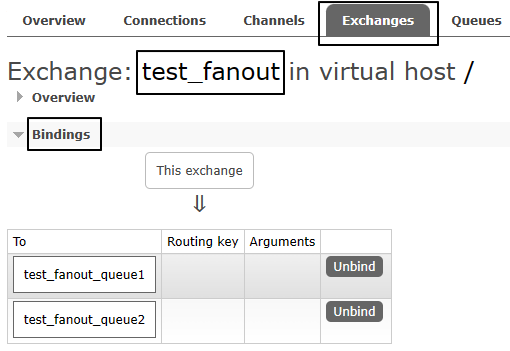
String exchangeName = "test_fanout";
channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName, BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT,true,false,false,null);
String queue1Name = "test_fanout_queue1";
String queue2Name = "test_fanout_queue2";
channel.queueDeclare(queue1Name,true,false,false,null);
channel.queueDeclare(queue2Name,true,false,false,null);
channel.queueBind(queue1Name,exchangeName,"");
channel.queueBind(queue2Name,exchangeName,"");
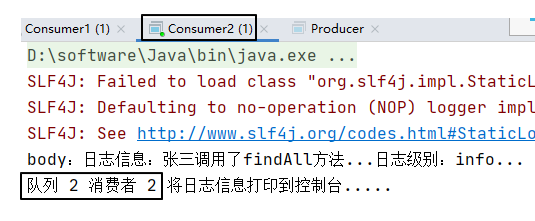
String body = "日志信息:张三调用了findAll方法...日志级别:info...";
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName,"",null,body.getBytes());
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
|